Nieuw bij Goldea? 15% kennismaking met code: FRESHSTART15
Reading time: 15 minutes
For years, the contraceptive pill has been the go-to method for many women to regulate their cycles, prevent pregnancy, or reduce skin problems. However, a shift is beginning to occur.
Did you know that fewer and fewer women are using the pill? According to the latest figures, contraceptive pill use in the Netherlands fell from 36% in 2012 to 28% in 2022.
More and more women are taking their They're examining their contraceptive use and are aware of the side effects. And that's a good thing!
Did you know that you don't have a natural cycle at all while taking the pill? In this blog post, we delve deeper into the often-overlooked side effects of the pill and what you can do to optimally support your body.
How does the pill work?
Most women know that the pill prevents them from getting pregnant, but what many people don't know is exactly how this happens.
The contraceptive pill contains synthetic versions of the female hormones Estrogen and progesterone. These hormones suppress ovulation, which tricks your body into thinking it's already pregnant and stops releasing eggs. Because of this, you actually have no natural cycle.
What you experience monthly during the stop week is Not a real period , but a withdrawal bleed. This is artificial bleeding that occurs in response to the hormones being stopped. But what else does the pill do to your body? Let's take a look at the side effects.
1. Irregular cycle
Some women take the pill to regulate their irregular cycle .
While the pill does indeed produce a predictable bleeding pattern, it often masks underlying hormonal imbalances .
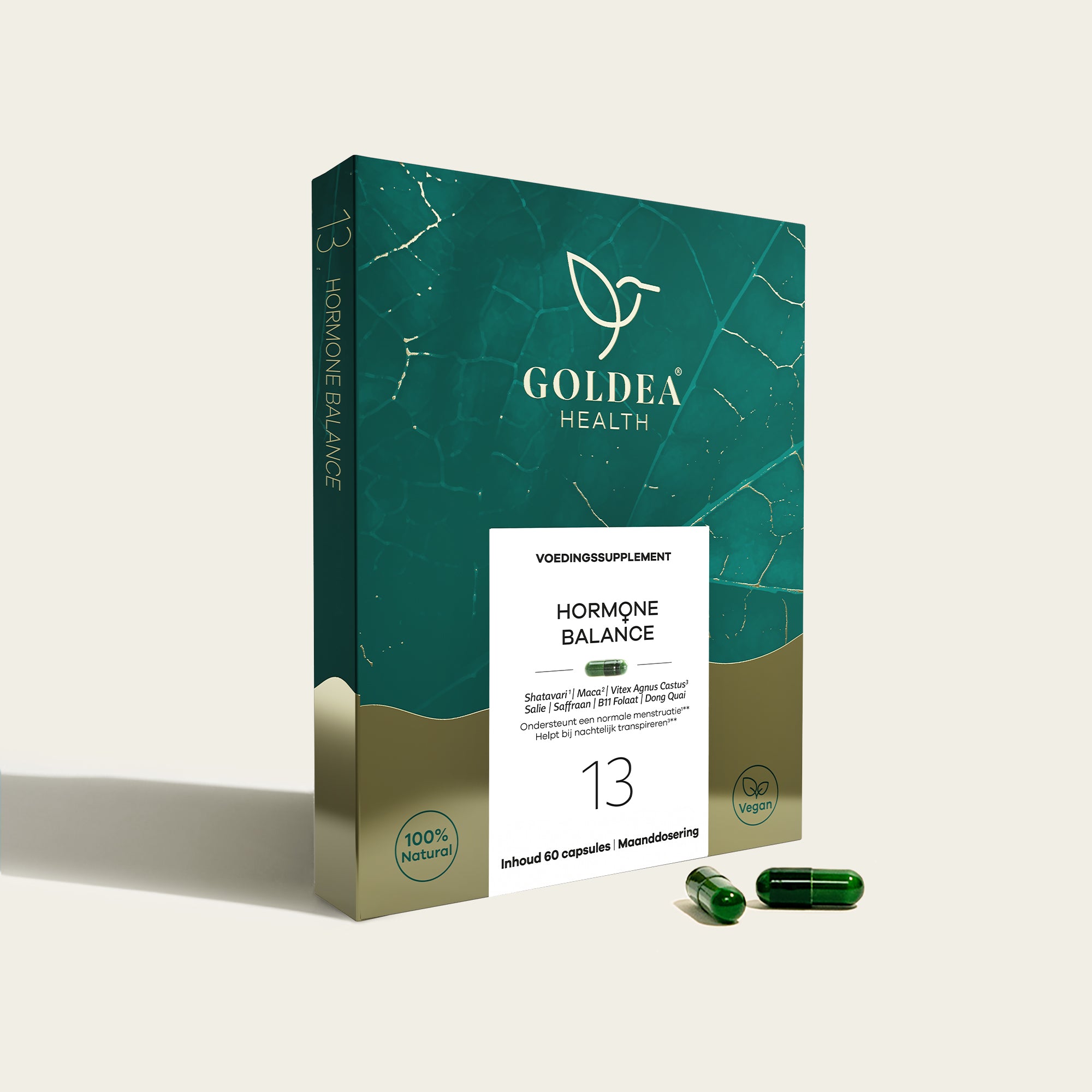
This imbalance will persist once you stop taking the pill. So it's a quick fix. This is where supplements like Hormone Balance is useful to bring your hormones back into balance.
2. Vaginal dryness
Estrogen plays an important role in maintaining the vagina's natural lubrication. However, the pill can reduce natural estrogen production , leading to vaginal dryness .
This can cause pain during sex and can also affect vaginal health . When this happens, it can be a sign that your body is producing too little estrogen. One solution could be to naturally support your estrogen with a supplement like Hormone Balance .
Note: As long as you're taking the pill, it will continue to affect your estrogen.
3. Vitamin and mineral deficiencies
It's less well known that the pill can interfere with the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals . B vitamins, magnesium , and zinc, in particular, are often not absorbed sufficiently by the body.
Zinc is essential for skin health, and a deficiency can lead to problems such as acne, especially after stopping the pill.
A good basis in terms of supplements is: Active B12 Complex , Power 5 Magnesium and Power 4 Zinc to, among other things, restore your zinc levels and prevent hormonal acne.
4. Nausea
A common complaint when starting the pill is nausea. This usually occurs because the hormones can irritate the stomach lining . This symptom often disappears after a few months, but if nausea persists, it may be helpful to take the pill with a meal or just before bedtime.
5. Headaches and migraines
Hormonal fluctuations can lead to headaches and, in some cases, migraines . For women who are prone to this, the pill can worsen the problem. Instead of continuing to struggle with headaches, it might be a good idea to switch to a non-hormonal form of birth control.
6. Bloating
Bloating and water retention are common complaints among women taking the pill. This is due to fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels , which can lead to changes in body weight.
7. Mood swings
The pill's impact on mood is often underestimated. Because the pill suppresses natural hormone fluctuations, many women experience mood swings. These can range from mild irritability to more serious symptoms of depression . If you notice your mood is negatively affected by the pill, it's important to discuss this with your doctor or therapist.
8. Weight gain
Many women report gaining weight after starting the pill. While the pill itself doesn't create fat, it can increase appetite and cause your body to retain more fluid. It's important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet.
9. Thrombosis and blood clots
A serious but rare side effect of the pill is an increased risk of blood clots, especially in women who take estrogen-containing pills .
This can lead to dangerous complications such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism. If you have an increased risk of blood clots, discuss with your doctor whether another non-hormonal form of contraception is more appropriate for you.
10. Less desire for sex
A low libido is a common complaint among women who use the pill. This is because the pill disrupts the natural hormone cycle and can reduce the production of testosterone , a hormone that plays an important role in sexual desire. By supporting your hormone balance with Hormone Balance , you may experience a greater desire for sex again.
11. Hair loss
The pill can disrupt the hair growth cycle , causing some women to experience hair loss. This is especially common in women who are sensitive to hormonal changes. If you notice your hair thinning , it's important to consider the pill's impact and consider natural ways to balance your hormones.
12. Fungal infections
Another common complaint is frequent yeast infections. This is because the pill can disrupt the vaginal flora , leading to an overgrowth of yeast. If you notice you're experiencing more frequent yeast infections, it may be wise to support the balance of your gut and vaginal flora with probiotics and consider stopping the pill.
13. Skin problems
Although the pill is often prescribed to treat acne , stopping it can actually lead to a return of pimples. The cause isn't being addressed; the problem is being suppressed .
This is also called "post-pill acne" and occurs because your body struggles to regain its natural hormone balance. Zinc plays an important role in skin health and can help reduce acne.
Tip: supplement with Power 4 Zinc can provide a natural solution to support your skin during this transitional period.
14. Pigment spots
The pill can increase your skin's sensitivity to sunlight , which can lead to pigment spots, especially on the face. This is called melasma and is more common in women with darker skin or a family history of pigmentation problems. Using a good (natural) sunscreen can help reduce this side effect.
15. Fatigue
Because the pill can disrupt the absorption of important nutrients , this can lead to fatigue . A deficiency of B vitamins in particular can lower your energy levels. It is therefore a good idea to Active B12 Complex to use to maintain your energy levels and prevent fatigue.
16. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
The pill can affect bowel function, leading to symptoms such as bloating, cramps, or diarrhea. If you already have IBS, the pill can worsen your symptoms.
Consider adjusting your diet (discuss this with a therapist) and using natural supplements that support gut health.
Tip: read the blog - Bloated stomach? 8 tips for healthy digestion
17. Sleep problems
Some women report that they sleep worse since starting the pill. This may be because the pill interferes with the natural production of melatonin , the sleep hormone .
Make sure you get plenty of relaxation and consider natural supplements such as Power 5 Magnesium to improve your sleep quality.
Tip: Read the blog - Sleep better with these tips - for even more sleep tips.
18. Less clear thinking
Some women notice that their cognitive functions, such as memory and concentration , are affected by the pill. This is also called brain fog .
While this isn't a widely discussed side effect, it can be a noticeable problem for some women. Taking supplements that support brain function, such as Vegan Omega-3 , can help keep your brain sharp.
Tip: read the blog - Healthy food for a well-functioning brain
19. Inflamed gums
Hormonal fluctuations, especially those caused by taking the pill , can affect your oral health and lead to inflamed gums or bleeding gums .
20. Increased risk of cancer
The pill can increase the risk of certain types of cancer , such as breast cancer. It's important to be aware of these risks and schedule regular checkups with your doctor.
What you can do:
- Using supplements such as Hormone Balance for hormonal support.
- Actively working on stress reduction through meditation, yoga, or relaxation techniques.
- Watch your diet with foods rich in essential vitamins and minerals + supplement with Active B12 Complex and Power 4 Zinc .
- Consult with your doctor about alternatives to the pill as contraception.